Study of Compounds – Ammonia and Nitric Acid
ICSE Grade 10 Chemistry - Chapter 9
📚 Smart Summary
1. Ammonia (NH₃) - Preparation
Laboratory Preparation: Heating ammonium salt with alkali. NH₄Cl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O + NH₃↑ (or Ca(OH)₂).
Setup: Round bottom flask heated gently. NH₃ collected by downward displacement of air (lighter than air) or over mercury.
Drying: Passed through CaO or quicklime (not conc. H₂SO₄ as NH₃ reacts with it forming (NH₄)₂SO₄).
Haber Process: Industrial preparation. N₂ + 3H₂ ⇌ 2NH₃ (at 450-500°C, 200 atm pressure, Fe catalyst).
Why Downward Collection: NH₃ is lighter than air (M = 17 < 29). Also very soluble in water (1:700), cannot collect over water.
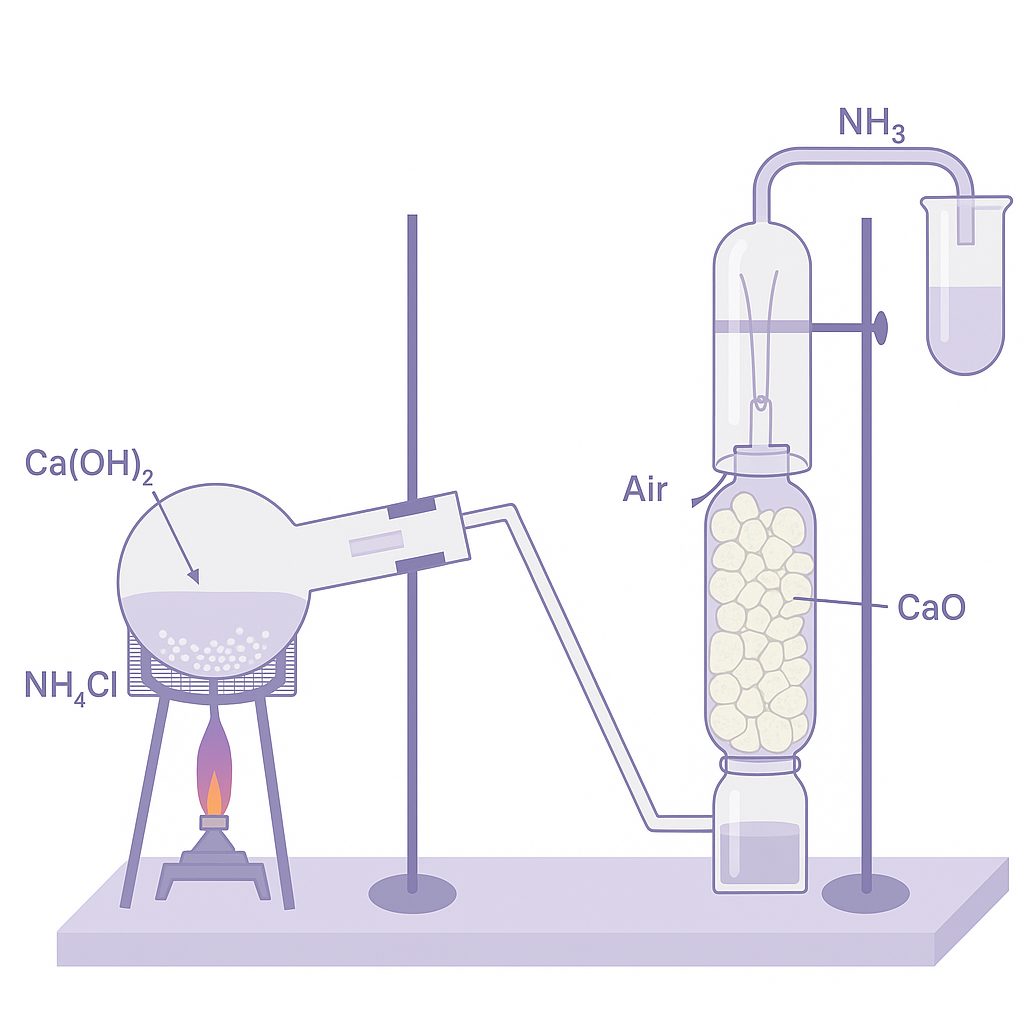
Laboratory preparation of ammonia gas using ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide
2. Properties of Ammonia
Physical: Colorless, pungent-smelling gas. Lighter than air. Highly soluble in water (fountain experiment).
Basic Nature: Turns red litmus blue. Forms NH₄OH in water: NH₃ + H₂O ⇌ NH₄OH ⇌ NH₄⁺ + OH⁻.
Test for NH₃: (1) Turns moist red litmus blue. (2) White fumes with HCl: NH₃ + HCl → NH₄Cl (white dense fumes).
With Acids: Forms ammonium salts. NH₃ + HCl → NH₄Cl, 2NH₃ + H₂SO₄ → (NH₄)₂SO₄.
Reducing Agent: 2NH₃ + 3CuO → 3Cu + 3H₂O + N₂ (reduces hot copper oxide to copper).
Uses: Fertilizers (NH₄NO₃, (NH₄)₂SO₄), refrigerant, cleaning agents, manufacturing HNO₃, explosives.
3. Nitric Acid (HNO₃) - Preparation
Laboratory: KNO₃ + H₂SO₄ → KHSO₄ + HNO₃↑ (heating potassium nitrate with conc. H₂SO₄).
Ostwald Process: Industrial method. 4NH₃ + 5O₂ → 4NO + 6H₂O (Pt catalyst, 800°C). 2NO + O₂ → 2NO₂. 4NO₂ + 2H₂O + O₂ → 4HNO₃.
Collection: All-glass apparatus (HNO₃ corrodes rubber). Cooled receiver to condense vapors.
Why All-glass: HNO₃ is highly corrosive and oxidizing, attacks rubber and cork.
Concentration: Distilled to get concentrated HNO₃. Pure HNO₃ is colorless, but often yellow due to dissolved NO₂.
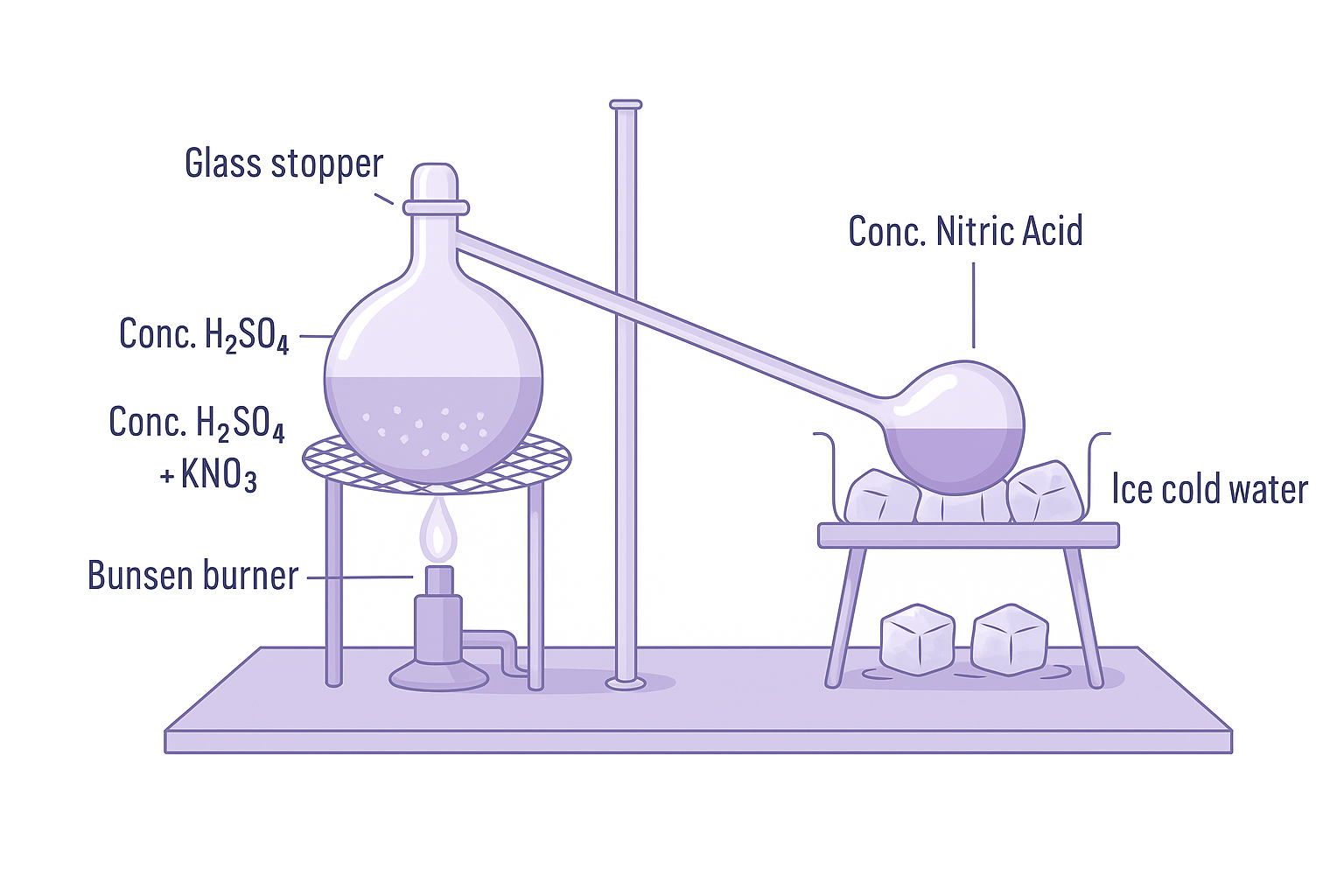
Laboratory preparation of nitric acid using potassium nitrate and concentrated sulfuric acid
4. Properties of Nitric Acid
Physical: Colorless liquid (pure), yellow if contains NO₂. Pungent odor. Fuming if highly concentrated.
Acidic Properties: Strong acid, completely ionized. HNO₃ → H⁺ + NO₃⁻. Turns blue litmus red.
Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer due to nascent oxygen. 2HNO₃ → 2NO₂ + H₂O + [O].
With Metals: With Cu: 3Cu + 8HNO₃ (dil) → 3Cu(NO₃)₂ + 4H₂O + 2NO↑ (brown fumes). Cu + 4HNO₃ (conc) → Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2H₂O + 2NO₂↑.
Aqua Regia: HCl:HNO₃ (3:1). Dissolves gold and platinum. Au + HCl + HNO₃ → AuCl₃ + NO + H₂O.
With Non-metals: Oxidizes P, S, C to their acids. 3P + 5HNO₃ + 2H₂O → 3H₃PO₄ + 5NO↑.
5. Ring Test and Uses
Brown Ring Test: For NO₃⁻ ions. Add FeSO₄ + conc. H₂SO₄ to solution. Brown ring at junction indicates NO₃⁻.
Reaction: NO₃⁻ + 3Fe²⁺ + 4H⁺ → NO + 3Fe³⁺ + 2H₂O. NO + FeSO₄ → [Fe(H₂O)₅NO]SO₄ (brown complex).
Uses of HNO₃: Manufacturing fertilizers (NH₄NO₃), explosives (TNT, nitroglycerin), dyes, plastics, medicines.
Uses of NH₃: Fertilizers, refrigerant, cleaning (household ammonia), manufacturing HNO₃, nylon, explosives.
Concentrated vs Dilute: Conc. HNO₃ gives NO₂ (brown fumes). Dilute HNO₃ gives NO (colorless, turns brown in air).
🎯 Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Ammonia is prepared in lab by heating:
Knowledge2. Ammonia is collected by:
Knowledge3. Ammonia is dried using:
Knowledge4. The test for ammonia gas is:
Knowledge5. In Haber process, ammonia is formed by:
Knowledge6. Nitric acid in lab is prepared from:
Knowledge7. Pure nitric acid is:
Knowledge8. The brown ring test is used to detect:
Knowledge9. Assertion (A): Ammonia turns red litmus blue. Reason (R): Ammonia is basic in nature.
Assertion-Reasoning10. Dilute HNO₃ reacts with copper to give:
Knowledge11. Concentrated HNO₃ reacts with copper to give:
Knowledge12. Aqua regia is a mixture of:
Knowledge13. The catalyst used in Ostwald process is:
Knowledge14. Ammonia acts as a reducing agent when it reduces:
Comprehension15. Which apparatus is used for HNO₃ preparation?
Knowledge16. Which gas is evolved when ammonium hydroxide is treated with lead nitrate?
Knowledge17. Assertion (A): Ammonia is collected by downward displacement of water. Reason (R): Ammonia is lighter than air.
Assertion-Reasoning18. What is the color of the flame when ammonia burns in oxygen?
Knowledge19. Which catalyst is used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid?
KnowledgePractice Numericals
Practice Problem 1: Calculate the mass of nitric acid produced from 8.5 g of ammonia in Ostwald process. (Atomic masses: N=14, H=1, O=16)
Application