Study of Compounds – Hydrogen Chloride
ICSE Grade 10 Chemistry - Chapter 8
📚 Smart Summary
1. Preparation of HCl
Laboratory Preparation: NaCl + H₂SO₄ → NaHSO₄ + HCl↑ (below 200°C). Heating common salt with conc. H₂SO₄.
Setup: Round bottom flask with delivery tube. NaCl is heated with conc. H₂SO₄. HCl gas collected by upward displacement of air (denser than air).
Drying: Passed through conc. H₂SO₄ (hygroscopic drying agent). Cannot use CaCl₂ (reacts with HCl).
Why H₂SO₄: Non-volatile, less volatile than HCl, displaces HCl from chlorides.
Industrial Preparation: Direct combination - H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl (in presence of sunlight).
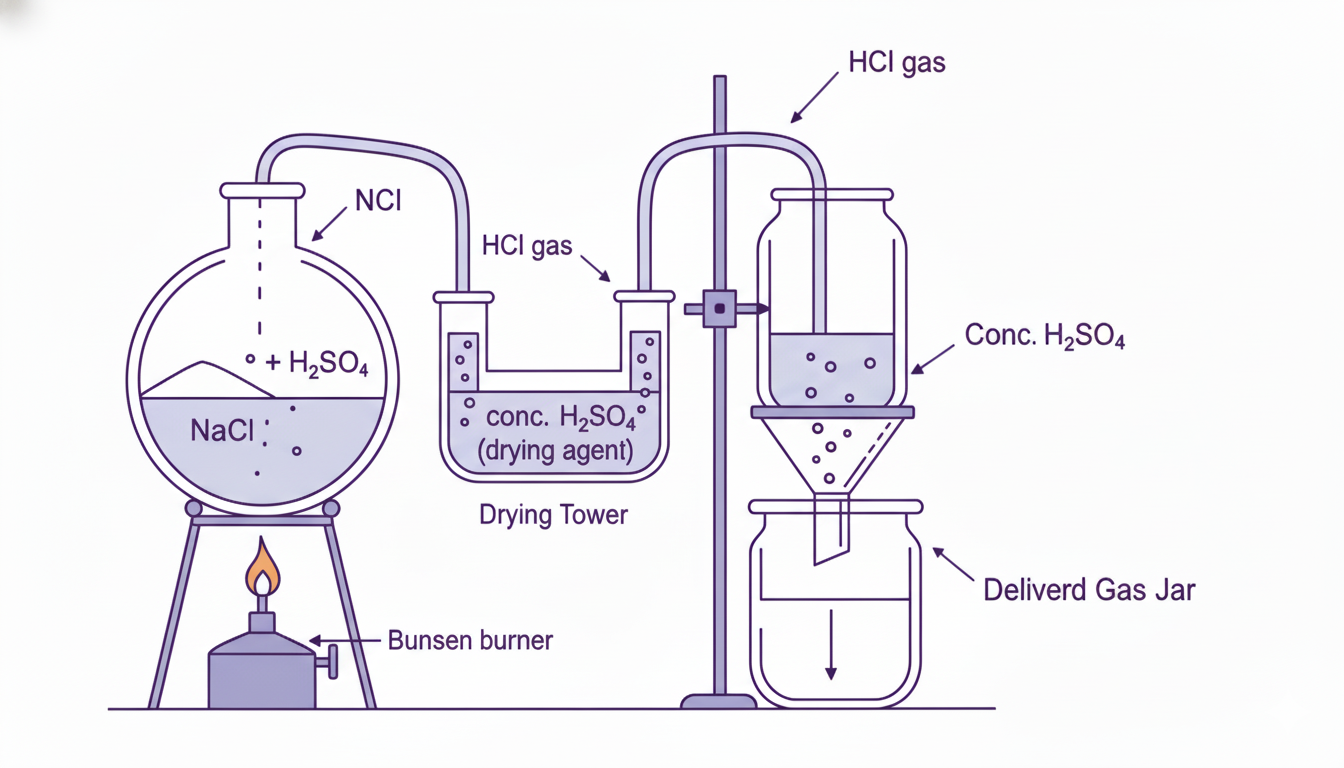
Laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas using sodium chloride and concentrated sulfuric acid
2. Properties of HCl
Physical: Colorless, pungent-smelling gas. Heavier than air (M = 36.5). Highly soluble in water (1:500 ratio).
Fountain Experiment: Demonstrates high solubility. Water rushes into flask containing HCl creating fountain effect.
Acidic Nature: Dissolves in water to form hydrochloric acid. HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻. Turns blue litmus red.
Chemical Properties: Reacts with NH₃ to form white fumes of NH₄Cl. HCl + NH₃ → NH₄Cl↓ (white fumes - test for HCl).
With Metals: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂↑. With Carbonates: CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂↑
Aqua Regia: HCl : HNO₃ in 3:1 ratio. Can dissolve noble metals like gold and platinum.
3. Tests and Uses
Test for HCl Gas: White fumes with NH₃. Glass rod dipped in NH₄OH held near HCl gives dense white fumes.
Test for Cl⁻ ions: AgNO₃ gives white precipitate of AgCl, soluble in NH₄OH. NaCl + AgNO₃ → AgCl↓ (white) + NaNO₃.
Uses: Manufacturing of aqua regia, cleaning metals (pickling), making chlorides, refining sugar, medicines.
Hydrochloric Acid: Aqueous solution of HCl. Strong mineral acid. Gastric juice contains dilute HCl (aids digestion).
🎯 Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice Questions
1. HCl is prepared in lab by heating NaCl with:
Knowledge2. HCl gas is dried using:
Knowledge3. HCl gas is collected by:
Knowledge4. The test for HCl gas is:
Knowledge5. Aqua regia is a mixture of:
Knowledge6. Assertion (A): HCl cannot be dried using CaCl₂. Reason (R): CaCl₂ reacts with HCl.
Assertion-Reasoning7. The molecular mass of HCl is:
Knowledge8. HCl is highly soluble in water because:
Comprehension9. The fountain experiment demonstrates:
Knowledge10. In industrial preparation, HCl is prepared by:
Knowledge11. HCl gas turns moist blue litmus:
Knowledge12. When HCl reacts with zinc, the gas evolved is:
Knowledge13. The white precipitate formed when AgNO₃ reacts with HCl is:
Knowledge14. Gastric juice in stomach contains:
Knowledge15. HCl is collected by upward displacement of air because it is:
Comprehension16. Which of the following is the correct laboratory preparation of HCl gas?
Knowledge17. Assertion (A): HCl gas is collected by upward displacement of air. Reason (R): HCl is lighter than air.
Assertion-Reasoning18. Which salt is formed when HCl reacts with ammonia?
Knowledge19. What happens when HCl gas is passed through blue litmus paper?
KnowledgePractice Numericals
Practice Problem 1: Calculate the volume of HCl gas produced when 5.85 g of NaCl reacts with excess H₂SO₄. (Atomic masses: Na=23, Cl=35.5)
Application